Last Updated on January 26, 2025 by
Electric vehicles have been on the rise in popularity in recent years. Many people are choosing to switch to electric cars due to their many benefits, such as lower emissions and cheaper operating costs.
However, one of the main questions people have about electric cars is how they heat the cabin.
In this blog post, we will explore how electric vehicles warm up the cabin and some of the different methods that are used. Stay tuned!
Key Takeaways about heating EV cabins
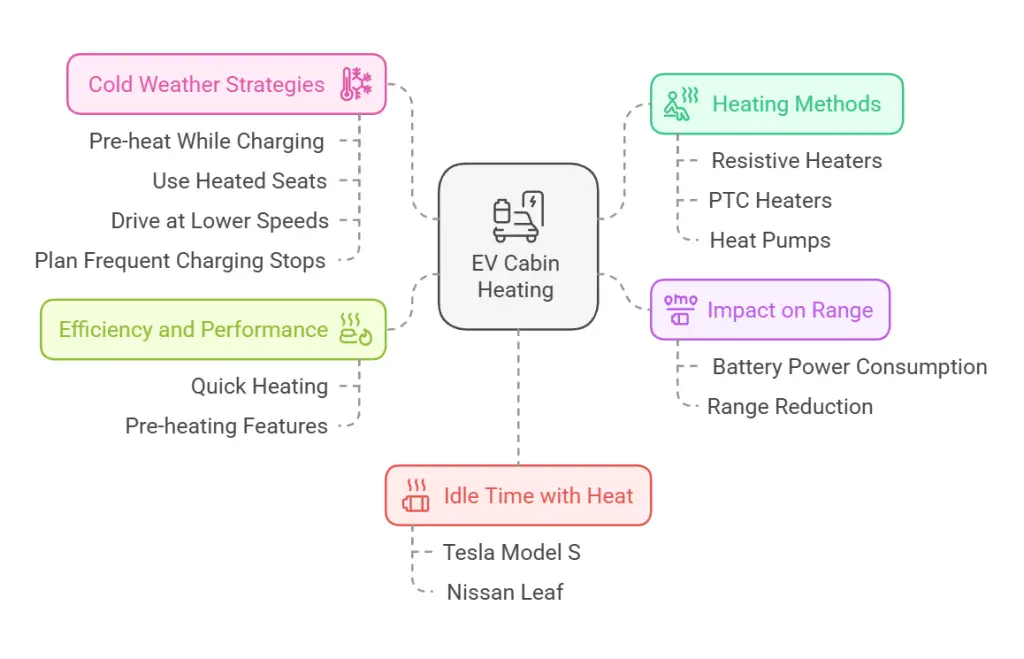
Electric vehicles (EVs) use two main methods for cabin heating: resistive heaters and heat pumps. Here’s a summary of how EV heating works:
- Heating Methods:
- Resistive heaters: Function like space heaters, using electricity to warm a metal coil.
- PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heaters: Self-regulating, reducing current as they warm up.
- Heat pumps: Most efficient, transferring heat from outside air into the cabin.
- Impact on Range:
- All heating methods consume battery power, reducing driving range.
- In cold weather, EV range can decrease by 10-30%, varying by model.
- Using the heater further impacts range, with potential reductions up to 41% in very cold conditions.
- Efficiency and Performance:
- Heat pumps are most efficient, generating 3-4 units of heat per unit of electricity.
- EVs typically heat up faster than gas cars, often within a minute.
- Many EVs offer pre-heating features while plugged in, preserving battery charge.
- Cold Weather Strategies:
- Pre-heat the cabin while charging
- Use heated seats instead of cabin heating
- Drive at lower speeds
- Plan for more frequent charging stops
- Idle Time with Heat:
- Varies based on battery size and conditions
- Example: Tesla Model S (100 kWh battery) can idle up to 12 hours, Nissan Leaf (40 kWh) about 4 hours
Overall, while EV heating systems are efficient, they do impact range, especially in cold weather. However, with proper strategies, EV owners can manage heating needs effectively.
How do heaters in electric cars work?
Electric cars use three primary heating methods: resistive heaters, PTC heaters, and heat pumps. Resistive heaters run electricity through a conductor to generate heat, similar to a space heater. PTC heaters self-regulate their temperature, reducing current as they warm up. Heat pumps are the most efficient, using refrigerant compression to transfer external heat into the cabin.
Key Heating Technologies for EVs
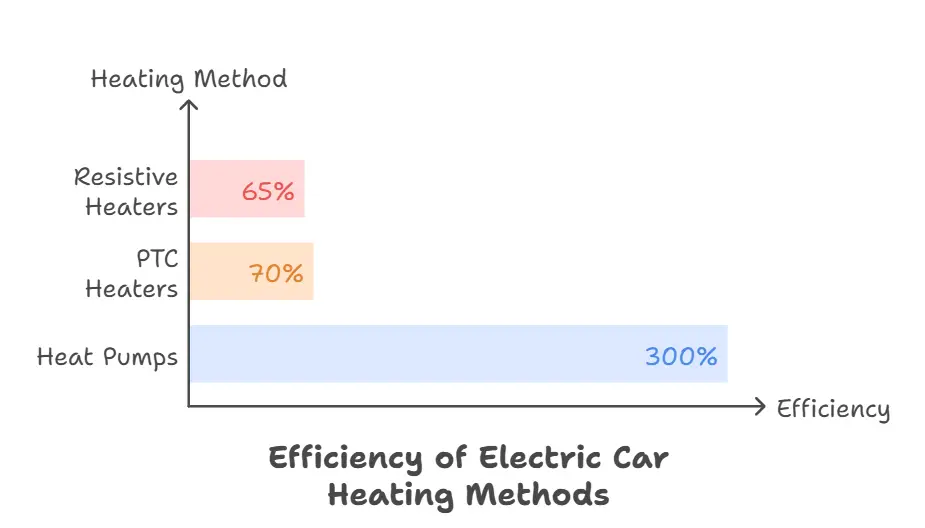
Heating Methods:
- Resistive Heaters: Convert electrical energy directly into heat (60-70% efficiency)
- PTC Heaters: Self-regulating with increased electrical resistance as temperature rises
- Heat Pumps: Generate 3-4 units of heat per 1 unit of electricity
Important Consideration: All heating methods consume battery power, potentially reducing an electric vehicle’s driving range in cold weather.
The new test reveals electric cars are practically unusable in winter
No definitive test proves electric cars are unusable in winter. Norwegian Automobile Federation tests actually show varied results: some EVs like the HiPhi Z lost only 5.9% range, while others like the Polestar 2 lost up to 30% range in cold conditions.
Key insights from winter EV testing include:
- Range can drop 10-30% in cold weather
- Performance varies significantly by model
- Norway, with extremely cold climate, had 79.3% of car sales as electric in 2022[2]
Consumer Reports testing confirmed range reduction, finding approximately 25% range loss when driving at 70 mph in cold temperatures compared to mild weather.
The test, which simulates conditions that are common in Scandinavian countries, shows that electric cars are practically unusable in winter.
The findings are based on the fact that electric cars rely on batteries to power their motors. In cold weather, batteries lose their charge more quickly, and the range of electric cars is significantly reduced.
As a result, electric cars are sometimes unable to meet the demands of winter weather, and their drivers are forced to rely on other forms of transportation.
The new test is an important step in evaluating the viability of electric cars in colder climates.
Do EV batteries need to warm up?
EV batteries perform best within specific temperature ranges. In cold conditions, batteries experience reduced efficiency and range. Many electric vehicles use battery warming systems that activate before and during driving to optimize battery performance, ensuring proper chemical reactions and maintaining optimal battery health in low temperatures.
At extremely low temperatures like -10°C, an electric vehicle might use approximately 3-5% of its total battery capacity to warm the battery to its optimal operating temperature. The exact percentage depends on:
- Battery chemistry
- Vehicle’s thermal management system
- Ambient temperature
- Desired battery temperature range
- Battery’s initial state of charge
The battery warming process is crucial because cold temperatures can significantly reduce battery performance and efficiency. Modern EVs use sophisticated heat pump and liquid cooling systems to minimize energy consumption while quickly bringing the battery to its ideal operating temperature, typically around 20°C.
What is the best EV for cold weather?
several EVs perform well in sub-zero temperatures, though all experience some range loss. Here’s a summary of the best-performing EVs in cold weather, along with some facts and figures:
| EV Model | Range Retention in Cold | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hyundai Ioniq 5 | 97% | Equipped with heat pump, pre-conditioning, and heated seats |
| Audi E-Tron (Q8 E-Tron) | 84% | 16% range loss in freezing temperatures |
| Hyundai Kona | 84% | Equipped with heat pump and pre-heating features |
| Nissan Leaf | 82% | 18% range loss in freezing temperatures |
| Tesla Model 3, X, Y | 76% | 24% range loss in cold weather |
Does using the heater in electric car affect the range?
As an electric vehicle owner, I’ve learned that winter presents unique challenges for my Peugeot e-208. The heat pump, while efficient, significantly impacts my driving range. I quickly discovered that in cold temperatures, my vehicle’s range can drop by up to 35%, a stark reality for EV drivers.
My strategy for managing winter driving has become quite nuanced. I’ve developed a careful approach to heating: I start by fully activating the heating system, allowing the cabin to reach a comfortable temperature. This initial warm-up consumes some battery power, but it’s more efficient than constantly fighting cold air.
Once the cabin is warm, I switch to ECO mode. This clever technique allows me to maintain a reasonable temperature while minimizing energy consumption. The heat pump works efficiently, generating three to four units of heat for every unit of electricity used. However, I’ve noticed its effectiveness diminishes when temperatures drop below -10°C.
The key is adaptability. By understanding my vehicle’s heating system and making strategic adjustments, I’ve learned to embrace electric driving, even in the coldest winter months.
EV Range Reduction Calculator
Impact of Cold Weather on EV Range
When the outside temperature is 0°F (-17.8°C), the impact on an electric vehicle’s (EV) range is significant. At this temperature, EVs typically experience a substantial decrease in range compared to their rated range under optimal conditions.
Based on the data from Geotab’s analysis, at 5°F (-15°C), EVs drop to approximately 54% of their rated range. Since 0°F is slightly colder than this reference point, we can estimate that the range reduction would be even more severe, potentially dropping to around 50% of the rated range.
Perspective on Range Reduction
- An EV rated for 250 miles (402 km) of range would likely only achieve about 125 miles (201 km) in these conditions.
- This significant reduction is due to several factors:
- Energy required to heat the cabin to a comfortable temperature
- Battery thermal management system working to keep the battery at an optimal operating temperature
- Increased thickness of the battery’s electrolyte fluid in cold temperatures, making it more difficult to retain and transfer energy
It’s important to note that using the cabin heating system in these conditions will further reduce the range. According to AAA research, using the heating system in cold weather (20°F or -6.7°C) can decrease the range by up to 41%.
Strategies to Mitigate Range Loss
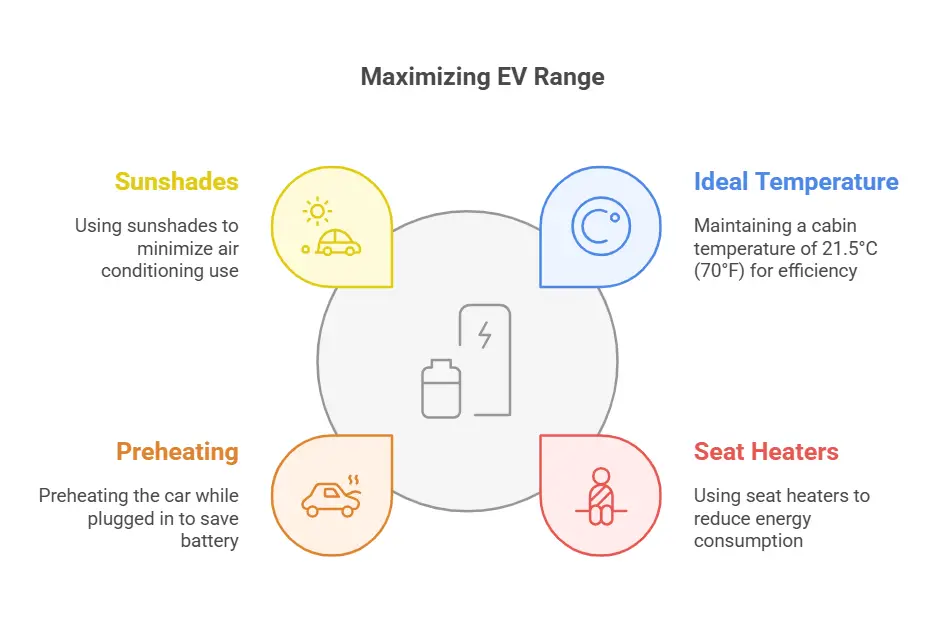
To mitigate range loss in such cold conditions, EV drivers can:
- Pre-heat the cabin while the vehicle is still charging
- Use heated seats instead of relying solely on cabin heating
- Drive at lower speeds to reduce aerodynamic drag
- Plan for more frequent charging stops on longer trips
By implementing these strategies, EV owners can better manage their vehicle’s range in extremely cold temperatures.
How long can an electric car idle with the heat on?
Electric cars can idle with heat on for varying durations depending on battery size. A Tesla Model S with a 100 kWh battery can potentially idle up to 12 hours, while a Nissan Leaf with a 40 kWh battery might idle around 4 hours. Factors like outside temperature and cabin heat settings significantly impact idle time.
As a result, electric car owners don’t have to worry about being left out in the cold or being uncomfortably hot on a summer day.
Do electric cars heat up faster?
Yes, electric cars heat up quickly, typically within a minute, using electric heaters similar to home radiators. Unlike gas cars that rely on engine coolant, EVs can generate heat rapidly and often offer pre-heating features through mobile apps, allowing cabin warming while the car is still plugged in and drawing mains power.
EV cold weather Reddit comments
Reddit often provides real user information, with no interest other than sharing information:
FAQ relating to heating electric vehicles
How do you heat the inside of an electric car?
Electric cars heat the interior using resistive heaters, heat pumps, or PTC heaters. Drivers can activate cabin heating through the car’s touchscreen or mobile app, often pre-heating the vehicle while still plugged in to conserve battery range during driving.
How does the heating work on an electric car?
Electric car heating uses three primary methods: resistive heaters (converting electricity directly to heat), PTC heaters (self-regulating temperature), and heat pumps (transferring external heat into the cabin). Each method consumes battery power but provides efficient interior warming.
How do electric cars cool the interior?
Electric vehicles cool interiors using air conditioning systems powered by the battery. These systems use refrigerant compression and expansion, similar to traditional cars, but are more energy-efficient. Climate control can be managed through the vehicle’s touchscreen interface.
How do Tesla cars heat the interior?
Tesla cars primarily use heat pumps for interior heating, which are more efficient than traditional resistive heaters. They can transfer heat from external air into the cabin, minimizing battery drain. Heated seats and steering wheels provide additional warmth.
Why does Tesla get so hot inside?
Tesla’s glass roof and large windows can create a greenhouse effect, trapping solar radiation. The car’s advanced climate control system can mitigate this by activating cooling systems automatically. Sunshades and tinted glass help reduce interior temperature buildup.
Do Tesla cars have radiators?
Tesla vehicles use a sophisticated thermal management system with liquid cooling, not traditional radiators. This system regulates battery, motor, and inverter temperatures, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Coolant circuits manage heat distribution throughout the vehicle’s critical components.
- Lavender Oil - February 2, 2025
- Electric Cars with Solar Panels On Roof: The Future of Sustainable Driving - January 29, 2025
- Best Cheapest Electric Car Reddit Comments - January 23, 2025