Last Updated on January 27, 2025 by
Electric vehicles (EVs) have more torque primarily due to their electric motors, which deliver maximum torque instantly from a standstill. This contrasts with internal combustion engines (ICE), which require time to reach peak torque. EVs achieve this through direct energy conversion and a simplified powertrain, enabling rapid acceleration and improved responsiveness.
An electric vehicle’s motor bypasses the lengthy process involved in internal combustion engines (ICE) to move the wheels. It generates torque instantaneously the moment you push the accelerator thanks to its relatively simple design.
Key Takeaways
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years, not only for their environmental benefits but also for their impressive performance characteristics. One of the most notable features of EVs is their high torque output, which contributes to their quick acceleration and overall driving experience. This document explores the reasons behind the higher torque in electric vehicles compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Understanding Torque in Vehicles
Torque is a measure of rotational force, and in the context of vehicles, it refers to the force that helps to turn the wheels. It is a critical factor in determining how quickly a vehicle can accelerate from a standstill. In traditional ICE vehicles, torque is generated through the combustion process, which involves a series of mechanical movements. In contrast, electric vehicles utilize electric motors that produce torque in a fundamentally different manner.
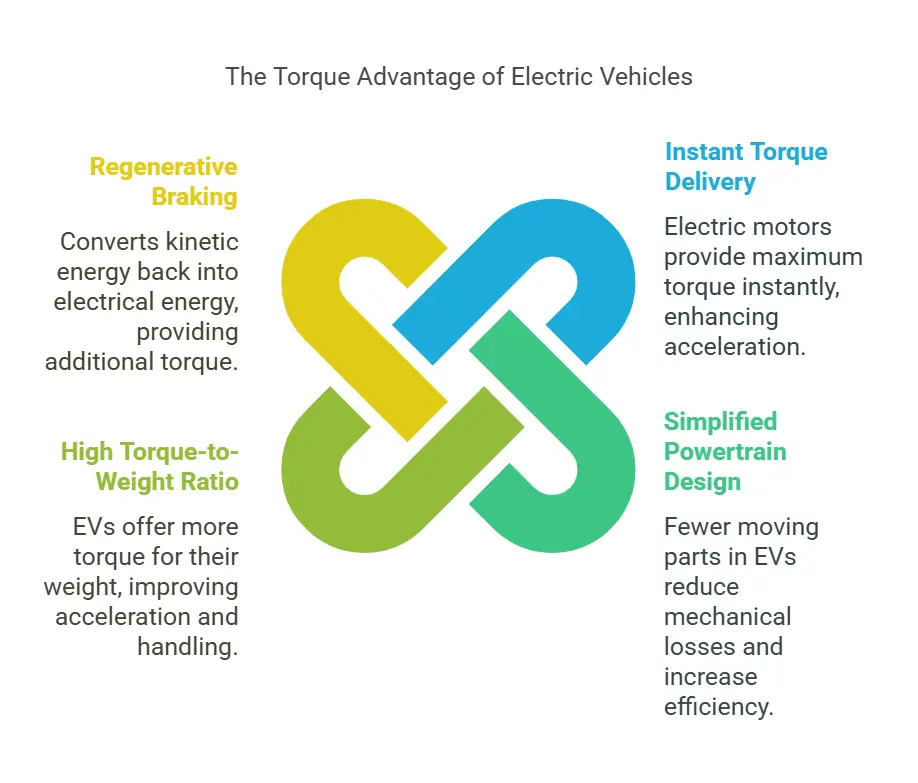
Instant Torque Delivery
One of the primary reasons electric vehicles have more torque is due to the nature of electric motors. Electric motors can deliver maximum torque instantly from a standstill, unlike ICE vehicles that need to build up RPMs to reach their peak torque. This immediate torque response allows EVs to accelerate rapidly, providing a thrilling driving experience.
Simplified Powertrain Design
Electric vehicles have a simpler powertrain design compared to traditional vehicles. An electric motor typically has fewer moving parts than an internal combustion engine, which reduces mechanical losses and increases efficiency. This simplicity allows for more effective torque delivery to the wheels, enhancing the overall performance of the vehicle.
High Torque-to-Weight Ratio
Electric motors are often lighter and more compact than traditional engines, which contributes to a higher torque-to-weight ratio in EVs. This means that for a given weight, electric vehicles can produce more torque, leading to better acceleration and handling. The placement of the battery pack in EVs also contributes to a lower center of gravity, improving stability and performance.
Regenerative Braking
Another factor that enhances the performance of electric vehicles is regenerative braking. This system allows the electric motor to act as a generator when slowing down, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. This process not only improves energy efficiency but also provides additional torque during acceleration, further enhancing the driving experience.
EV Torque Calculator
Compare Torque
Why Do Electric Motors Lose Torque at High RPM?
Electric motors lose torque at high RPM due to back electromotive force (back-EMF), which generates a counter-voltage that opposes the motor’s supply voltage. As speed increases, the effective voltage drops, reducing current and consequently torque production, leading to diminished power output at extreme rotational speeds.
The EV’s motor produces the power to turn the wheels by passing an electric current through its coils within a magnetic field. The more the windings and greater the capacity of the battery the better is the acceleration.
An ICE on the other hand generates torque by combustion of fuel to move the pistons and turn the crankshaft. The crankshaft transfers this power to the wheels via the transmission.
| RPM Range | Electric Motor Torque | ICE Torque |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Maximum (instant) | Low |
| Medium | High | Peak |
| High | Decreasing | Decreasing |
This process involves a time lag as the vehicle needs to rev up before it can gain the momentum to get into motion. An electric vehicle in contrast roars to life at full throttle without any delay as it transfers power directly to its wheels.
However, there’s a catch. The torque is inversely proportional to the speed of the vehicle measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
The age-old advice of slowing down when going uphill or while carrying a load is due to this reason. It means the quick acceleration is not sustainable over a period.
The electric motor’s rotations also generate a counter electromotive force (EMF).
The “back EMF” kicks in as the RPM increases after a certain duration of time has elapsed. It resists the supply voltage which slows down the EV motor’s torque generating capacity.
So the reason that electric motors lose torque at high RPM is:
- Torque reduces as the speed increases
- The EV motor generates a back EMF impeding the supply voltage
Do Electric Motors Have More Torque Than Diesel?
Electric motors generally have higher torque than diesel engines, especially at low RPMs. They can deliver maximum torque instantly, allowing for rapid acceleration without needing to reach higher speeds. Diesel engines, while known for their strong torque output, typically produce peak torque at specific RPM ranges and require higher engine speeds to achieve optimal performance.
Yes, electric motors generate more torque than diesel engines. Imagine a row of vehicles including electric and gas and diesel-powered vehicles at a red light at a busy intersection.
The light changes to green after some time and the EV zips ahead of the pack in an instant. You wonder if an EV’s motor packs more power than a conventional ICE automobile.
| Characteristic | Electric Motor | Diesel Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Torque at 0 RPM | Maximum | Minimal |
| Acceleration from standstill | Instant | Gradual |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Mechanical complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Emissions | Zero | High |
Well, not exactly. It’s the EV’s superior torque or rotational force that moves a car from a stationary position, which makes a difference.
The more the torque the better is the acceleration capacity of a vehicle from a stationary position.
An EV’s motor has a unique capacity to produce maximum torque at zero RPM.
The rotor within the motor is connected to a single gear and the acceleration is instantaneous when you press the pedal. What’s more the EV’s torque does not have to contend with the thousands of parts in a diesel-powered vehicle.
The electric motor is also lighter which boosts its torque considerably. So you don’t have to worry about friction and oily soot.
Nor do you need to have any concern about smelly and toxic exhaust fumes poisoning the environment.
A diesel engine on the other hand has to shift to a lower gear to generate the torque to gain momentum.
An electric motor is not impeded by this condition.
So electric motors outperform diesel engines in terms of torque as:
- An EV’s motor is able to generate torque at zero RPM
- An electric motor is lighter than a diesel engine
- The motor works on a simpler and direct principle to generate power
What Is an EV Torque Curve?
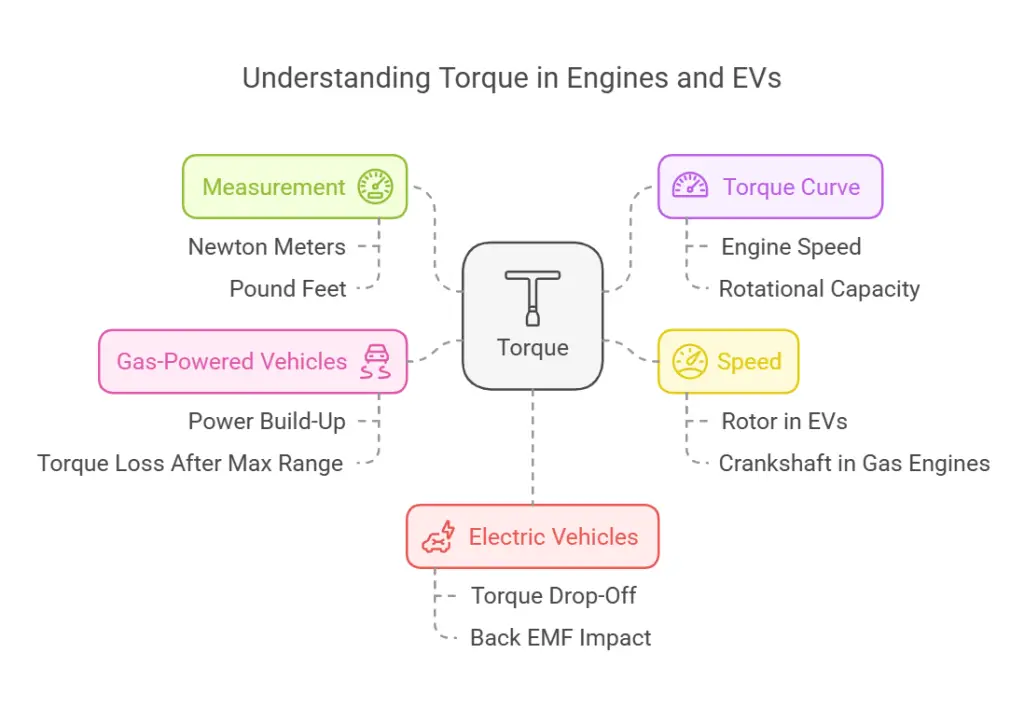
An EV torque curve illustrates the relationship between the torque produced by an electric motor and its rotational speed (RPM). Typically, it shows maximum torque at low speeds, which gradually decreases as speed increases. This curve is divided into two main regions: the constant torque zone, where maximum torque is sustained, and the constant power zone, where torque decreases while power remains stable.

- Torque is a twisting force that is applied at a distance.
- The torque of an engine is measured in Newton meters (Nm) or pound feet (lb-ft) to denote its pulling capacity.
- The torque curve plots an engine’s speed and its torque or the rotational capacity on a graph.
- The speed is measured in revolutions per minute (RPM) of the rotor in an EV’s motor or the crankshaft in a gas-powered engine, as it rotates around its axis.
- Torque is inversely proportional to speed after a certain time lag. So the more the speed the less the torque and vice versa.
- A gas-powered vehicle’s torque curve rises gently as the engine slowly builds power.
- An EV’s motor’s curve on the other hand begins from peak torque capacity at zero speed and then drops off as the speed increases.
- This torque generation capacity loses force after the power output reaches its maximum range.
- In an EV motor, the back EMF also reduces its torque.
What Is Instant Torque?
Instant torque is an electric vehicle’s ability to deliver maximum rotational force immediately at 0 RPM, unlike internal combustion engines that require time to build up power. This occurs because electric motors convert electrical energy directly into mechanical motion through magnetic field interactions, enabling rapid, seamless acceleration from a standstill.
The EV motor can achieve maximum torque from zero revolutions per minute (RPM). This phenomenon is known as instant torque.
There’s no clutch or gearbox involved and the motor directly powers the wheels without having to go through any intermediary.
This is why you are thrown back in your seat when you hit the pedal to accelerate while driving an EV. The capacity enables an EV to get off the blocks in the blink of an eye, something which no gas-powered vehicle can aspire to do.
Tesla Electric Motor Torque Curve
A Tesla’s torque generation capacity does not tail off as quickly other EVs. The secret lies in its motor design.
- The motor connects to the battery via a drive unit which regulates the torque, speed and power by controlling the voltage and current.
- An onboard computer runs this process to ensure that the motor functions at an optimum level to avoid overheating.
- A Tesla’s motor is quite efficient in its power distribution, using about 60% of electrical energy generated to gain momentum.
- A gas-powered vehicle uses only about 20% of the power generated to move the wheels considering the loss of energy in the combustion process.
Tesla Electric Motor Characteristics
- Instant Torque Delivery: Tesla electric motors provide maximum torque from 0 RPM, allowing for rapid acceleration. This feature is particularly noticeable in models like the Tesla Model S and Model 3, which can achieve 0-60 mph in just a few seconds.
- Flat Torque Curve: The torque curve of Tesla motors is relatively flat over a wide range of RPMs. This means that the vehicle can maintain strong acceleration without significant drops in torque as speed increases, unlike traditional engines that may have a peak torque range.
- Regenerative Braking: Tesla vehicles utilize regenerative braking, which not only helps to recharge the battery but also allows the electric motor to act as a generator, providing additional torque when slowing down.
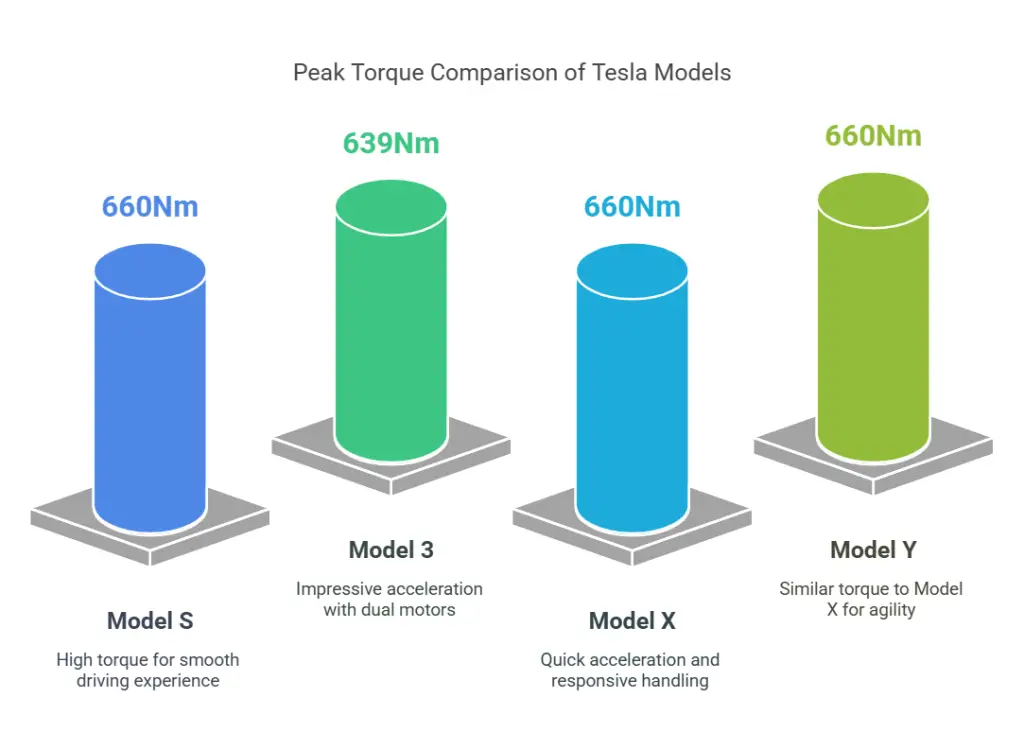
Torque Curve Analysis
Model S
- Peak Torque: The Model S electric motor can produce peak torque of approximately 660 Nm (Newton-meters).
- Torque Delivery: The torque remains high across a broad RPM range, providing a smooth and powerful driving experience.
Model 3
- Peak Torque: The Model 3’s dual motor setup can achieve peak torque of around 639 Nm.
- Acceleration: The vehicle’s torque curve allows for impressive acceleration, with a 0-60 mph time of as little as 3.1 seconds in the Performance variant.
Model X and Model Y
- Torque Characteristics: Both the Model X and Model Y feature similar torque curves, with peak torque figures around 660 Nm, enabling quick acceleration and responsive handling.
How Much Power Does an Electric Car Have?
Electric cars have a wide range of power outputs, typically from 100 to over 1,000 horsepower. High-performance models like the Lucid Air boast up to 1,234 hp, while more common EVs like the Tesla Model 3 Performance offer 510 hp. Power output largely depends on the battery pack and motor configuration.

Electric vehicles can cover 100 kilometers with 15 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy on an average. The power output depends on the motor’s size and the battery’s wattage.
The power denotes the amount of energy produced in a given timeframe. This has a bearing on how much load will the car be able to carry.
- Can it go uphill on steep inclines?
- Can it traverse through muddy tracts?
- Can it carry heavy loads?
For example, the Tesla Model S can zoom to 100 kilometers per hour from a standing position in an astonishing 1.98 seconds courtesy its 100 kWh battery. It performs great in going uphill however the car won’t be able to pull tons of metal or produce.
As with any engine, the EV motor does not use all the energy it produces. Some energy is lost due to heat and as the battery “ages.”
FAQ Relating to Electric Vehicles and More Torque
Do Electric Cars Have Higher Torque?
Yes, electric cars generally have higher torque than gasoline-powered vehicles. Electric motors deliver maximum torque instantly from zero RPM, providing rapid acceleration from a standstill. This contrasts with internal combustion engines, which require higher RPMs to reach peak torque. Electric vehicles’ instant torque contributes to their swift acceleration and overall performance.
Electric cars have considerably higher torque than gas or diesel-powered vehicles. Electric cars are well known for shooting off like an arrow from a standing position.
This quality is an expression of its torque.
An EV’s motor can touch its peak torque capacity with zero speeds. This is possible due to:
- Battery capacity
- Electric motor design
- Direct application of force
The torque or twisting force of an EV’s motor is not dependent on gears and transmission. A powerful battery of more than 100 kWh runs the rotor within the EV motor.
The rotor is connected to a shaft that provides the momentum to the car’s wheels. The transfer of power is direct and without the need to assemble pistons and cranks to generate the mechanical force to move the vehicle.
A single gear connected to the rotor ensures that energy is provided to the wheels the moment you press the pedal. So there’s no need to rev up the car or to change gears after turning on the ignition.
An added advantage is that the rotor can also operate in the reverse direction and function as a generator. The motor drives the wheels while you are pushing the throttle and the wheels drive the motor when you slow down.
This phenomenon is known as regenerative braking.
How Do Electric Cars Get Instant Torque?
Electric cars achieve instant torque through their motor design. They convert electrical energy directly into mechanical motion, creating immediate magnetic field interactions. This allows maximum torque production from 0 RPM, unlike combustion engines. The simplified drivetrain and lighter components further enhance the instant torque delivery, enabling rapid acceleration from a standstill.
A battery already has the energy stored within it which is instantaneously transferred to the wheels via the motor.
Gas-powered vehicles on the other hand have to first generate the required energy before it can be transferred to the wheels via the transmission.
So there’s no delay involved after you power the electric vehicle. All that’s needed is a fully charged battery, and you are first out of the gates.
The right voltage and current take the place of the gears and drive to generate the torque. If you want more power and torque you don’t need to add leverage in the form of gears or a bigger motor with more pistons.
The torque’s value is dependent on the current and the coils in the motor.
An electric car comes with an inbuilt controller to regulate the current and avoid overheating of the windings. This is a vital feature as the electric motor needs frequent cooling similar to how the radiator works in a gas-powered vehicle.
Why Does Tesla Have More Torque?
Tesla vehicles have more torque due to their electric motor design. They deliver maximum torque instantly from zero RPM, unlike internal combustion engines. Tesla’s motors use advanced technologies like permanent magnet synchronous motors and optimized rotor designs, enabling rapid acceleration. The simplified drivetrain and lighter components further enhance torque delivery, resulting in superior performance from a standstill.
An electric motor’s functioning is entirely different from an ICE vehicle. The torque is more readily available in electric cars than it’s accessible for gas-powered vehicles.
So how does it work?
- The motor starts off with full power when it’s connected to the battery source providing the vehicle with all the torque it needs to gain momentum from a state of inertia. Say goodbye to the clutch and gearbox.
- The current flowing through the electric motor initiates an electrical charge which causes an armature in the motor to rotate.
- So when you press the accelerator the desired speed is immediately attained without any interference from gear changes.
- The EV motor’s inbuilt software ensures that the speed does not cross the maximum limit preventing overheating and damage to the engine.
This feature is not available for the conventional gas-powered vehicles and that’s why you need to idle the vehicle first thing in the morning especially during winter.
The best part of driving an EV is that you don’t even feel the power coursing through the car. A smooth and silent ride is the hallmark of driving an electric vehicle.
Why Do Electric Vehicles Have More Torque – Reddit Comments
Research Papers on the Subject of EV Torque
- A study published in the World Electric Vehicle Journal in 2021 examined the torque characteristics of a 2 kW BLDC motor used in the KMLI E-Falco electric car.
- A paper in Electronics (MDPI) from May 2024 investigated the torque characteristics of vehicle motors under various conditions, including temperature rise and multisource excitation.
- A recent study published in Nature’s Scientific Reports on June 28, 2024, presented a novel electric vehicle traction motor control system based on a robust predictive direct torque control approach.
Future Developments in EV Torque
The electric vehicle (EV) industry is rapidly evolving, with advancements in technology driving significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and sustainability. One of the critical areas of focus is torque, which plays a vital role in the overall driving experience and vehicle dynamics. This document explores the future developments in EV torque, highlighting innovations in motor design, battery technology, and control systems that promise to enhance torque delivery and efficiency in electric vehicles.
Advances in Motor Design
The design of electric motors is crucial for optimizing torque output. Future developments are likely to focus on:
- Permanent Magnet Motors: Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes are expected to enhance the efficiency and torque density of permanent magnet motors. This could lead to lighter and more compact motors that deliver higher torque at lower speeds.
- Switched Reluctance Motors (SRMs): SRMs are gaining attention due to their simplicity and robustness. Future advancements may improve their torque characteristics and control strategies, making them a viable alternative to traditional motor types.
- Integrated Motor-Drive Systems: The integration of motor and drive electronics can reduce weight and improve efficiency. Future designs may leverage advanced cooling techniques and compact packaging to enhance torque performance.
Battery Technology Enhancements
The relationship between battery technology and torque delivery is critical. Future developments may include:
- Higher Energy Density Batteries: As battery technology progresses, higher energy density batteries will enable more power to be delivered to the motor, resulting in improved torque performance.
- Fast Charging Capabilities: Innovations in fast charging technology can ensure that batteries maintain optimal performance levels, allowing for consistent torque delivery during high-demand situations.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Advanced BMS will play a crucial role in optimizing torque output by managing battery health and performance, ensuring that the vehicle can deliver maximum torque when needed.
Control Systems and Software
The evolution of control systems is essential for maximizing torque efficiency and responsiveness. Future developments may include:
- Advanced Torque Vectoring: This technology allows for the distribution of torque to individual wheels, improving traction and handling. Future systems may utilize machine learning algorithms to adapt torque distribution in real-time based on driving conditions.
- Predictive Control Algorithms: By analyzing driver behavior and road conditions, predictive control systems can optimize torque delivery, enhancing both performance and energy efficiency.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: Integrating V2X technology can provide real-time data on traffic and road conditions, allowing for smarter torque management and improved overall vehicle performance.
Conclusion – What does the future hold for EV Torque?
The future of EV torque is poised for significant advancements driven by innovations in motor design, battery technology, and control systems. As the industry continues to evolve, these developments will not only enhance the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles but also contribute to a more sustainable and enjoyable driving experience. The ongoing research and investment in these areas will be crucial in shaping the next generation of electric mobility.
- Lavender Oil - February 2, 2025
- Electric Cars with Solar Panels On Roof: The Future of Sustainable Driving - January 29, 2025
- Best Cheapest Electric Car Reddit Comments - January 23, 2025